Intracellular hormone receptors
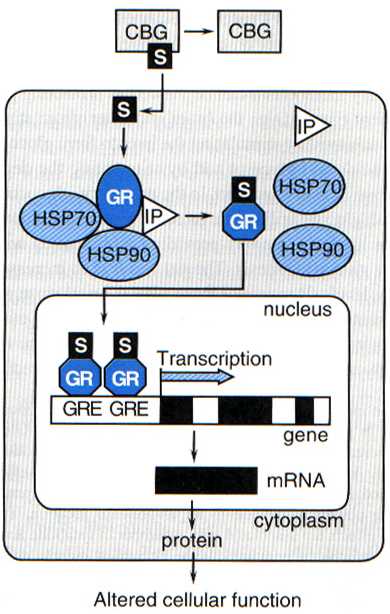
Intracellular mechanism of action of the glucocorticoid receptor. The molecular pathway by which glucocorticoid steroids (labeled S) enter cells and interact with the glucocorticoid receptor to change the GR conformation (indicated by the change in shape of the GR), induce GR nuclear translocation, and activate transcription of target genes is shown. The example shown is one in which glucocorticoids activate expression of target genes; the expression of certain genes, including proopiomelanocortin (POMC) expression by corticotropes, is inhibited by glucocorticoid treatment. CBG, corticosteroid binding globulin; GR, glucocorticoid recptor; S, steroid hormone; HSP90, 90-kDa heat shock protein; HSP70, 70-kDa heat shock protein; IP, 56-kDa immunophilin; GRE, glucocorticoid-response elements in the DNA that recognize and bind the GR, thus providing specificity to induction of gene transcription by glucocorticoids. Within the genes are introns (unshaded) and exons (shaded); transcription and mRNA processing leads to splicing and removal of introns and assembly exons into mRNA.
